What does Forex mean and what is behind the Forex market?
Anyone who has ever traveled knows the small exchange rate counters at airports. There you can exchange your money from your home country into the local currency of the country you are visiting. And if you have already made such a trade, you have already been active in the Forex market. Because Forex (FX) stands for Foreign Exchange Market and means nothing more than trading in foreign exchange. The Forex market is huge and has a daily trading volume of over 4 trillion USD. With foreign exchange trading, just like with stocks, you can make corresponding price gains and also price losses, as exchange rates are subject to fluctuations. For example, if it goes of the European economy is good and that of the USA rather bad, then the rate for EUR/USD rises, i.e. for one euro you get more USD.
The Forex Market
Constantly, in the globalized world, bills have to be paid in different currencies and these constant account movements cause the price of currencies to be constantly renegotiated. And to ensure that this happens as quickly as possible, the banks are linked via computer networks. And it is in these networks that the price of a currency is virtually set. And this happens when the person who wants to spend money compares prices and buys where the situation says it is cheapest. By the way, the exact technical term for this is Electronic Communications Network. The world’s largest network is provided by Currenex. The broker that offers a trader a Currenex connection is also really directly present on the Forex market. However, many brokers only offer the Metatrader trading platform, which is also very comprehensive and widely used, but unfortunately often does not provide access to Currenex. Such brokers operate as market makers and determine the prices themselves, which is often done to the disadvantage of traders.
The most important players in the Forex market are certainly large credit institutions, but also industrial companies,trading companies as well as private Forex traders provide a highly liquid market. A significant influence on the foreign exchange market is also exerted by the central banks, whose monetary policy measures can strongly influence the exchange rates between the individual currencies.
Financial Markets
There are various financial markets on which trading takes place. In the field of Forex trading, the relevant financial market is the foreign exchange market. In addition to this market, there is also the money market and the capital market.
The money market mainly trades overnight or term money, so it is well suited for short-term investments. The capital market is divided into the bond market and the stock market. As a normal investor, you either buy shares in a company or invest your money in equity funds. The foreign exchange market is the market where receivables (money, checks, book money) are traded in different currencies. Currency pairs are always traded on the foreign exchange market. The first part A is called base currency and B stands for quote currency. If you want to buy as a currency pair, you buy the base currency and sell the quote currency. The exchange rate value indicates how much of the quote currency is needed to purchase one unit of the base currency.
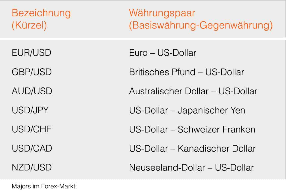
Exotic currency pairs (crosses)
These currencies are not traded against the US dollar as the reserve currency. In addition to the dollar, the euro and the Japanese yen are the most important currencies in the foreign exchange market, as these are also often held as currency reserves by various nations or central banks. Therefore, various euro and yen crosses without dollar participation are also traded with high turnover, such as EUR/GBP, EUR/JPY, GBP/JPY or EUR/CHF. In contrast to these highly liquid crosses, exotic currency combinations also exist, which may be more difficult or risky to trade due to the much lower liquidity. However, monitoring the exotics may well prove useful in gaining insights for the majors’ actions from the analysis of relative strength. If the question is whether to buy AUD/USD or NZD/USD, it might be worth taking a look at AUD/NZD. For example, if AUD/NZD just broke out of a sideways move to the upside, AUD/USD is preferable to NZD/USD due to relative strength.
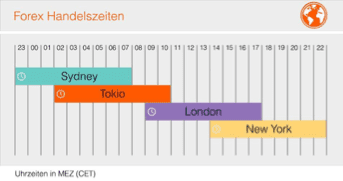
Trading hours
Trading on the Forex market is actually possible around the clock. So 24 hours a day. However, of course, not always the same amount moves. Roughly speaking, there are four main trading hours: Sydney time, Tokyo time, London time and New York time.
How is money earned?
Ex. the EUR/USD rate stands at 1.3070! The share price is now expected to rise because, for example, unemployment figures are falling in Europe. So you open a buy trade at 1.3070! After a few hours, the rate is at 1.3075, which means it has increased by 5 pips. Now you close the trade and realize the 5 pips profit. Depending on how much you put into the trade, a pip means more or less money. So for example 1 Euro or 10 Euro. How much is the profit/loss is explained below. In return, however, you can also bet on falling prices. The EUR/USD rate is back at 1.3070! The price is now expected to fall because, for example, unemployment figures have risen in Europe. So you open a sell trade at 1.3070! After a few hours, the rate is at 1.3065, i.e. it has fallen by 5 pips. Now you close the trade and realize 5 pips profit again.
Pips, Lot and the Leverage
A pip is, as already mentioned, the last decimal place of the exchange rate. However, a pip has a different value because it depends on the lot size. A lot indicates the unit of measure of a traded currency; in the case of EUR/USD, the reference is to the euro. There are different lot sizes that can be traded. By default, a lot is often 100,000, but there are also mini lots with 10,000! So if you want to trade the EUR/USD, you buy 1 lot, that is for 100,000 euros. That sounds a lot at first, but of course you don’t have to spend that much money yourself. One trades quasi with a lever, i.e. in order to trade the 100,000 euro, one must use e.g. only 2,000 euro oneself. The forex broker sort of lends you the 100,000 and requires a margin of a few percent as collateral, this varies from broker to broker. The forex broker sort of lends you the 100,000 and requires a margin of a few percent as collateral, this varies from broker to broker. 1 pip for EUR/USD = 0.0001.
(1 pip / rate) x lot = profit per pip in the respective currency
(0.0001 / 1.3070) x 100,000 euros = 7.65 euros
So if you would make 5 pips profit, you would have earned 38,25 Euro with the trade. On the 2,000 euros that you only have to bring, that would be a return of 1.9%! It doesn’t sound like much at first, but if you consider that it takes several years to make 2% on a savings account and only one trade here, i.e. a few hours, it’s a lot! I.e. if you would make 2% every day and reinvest the earned money right away, after 200 successful trades (let’s say in 200 days) you would have increased the 2,000 Euro to 100,000 Euro.
